Thrombosis
The Mechanism of Blood Clot
What kind of blood vessel likely to clot?
Blood in normal condition does not clot in blood vessels, and it clots when an injury occurs and the blood gets outside of the vessel. In another words, blood vessel that forms thrombus easily in your body has abnormalities. According to Virchow, the 19th century pathologist, he said three factors are involved to this function: “blood,” “blood vessels,” and “blood flow” (*).
*Tetsumei Urano, Yuko Suzuki, Hayato Ihara, Hideo Mogami
Risk factors for thrombosis: components in blood and on vascular endothelial cells
Changes in Blood
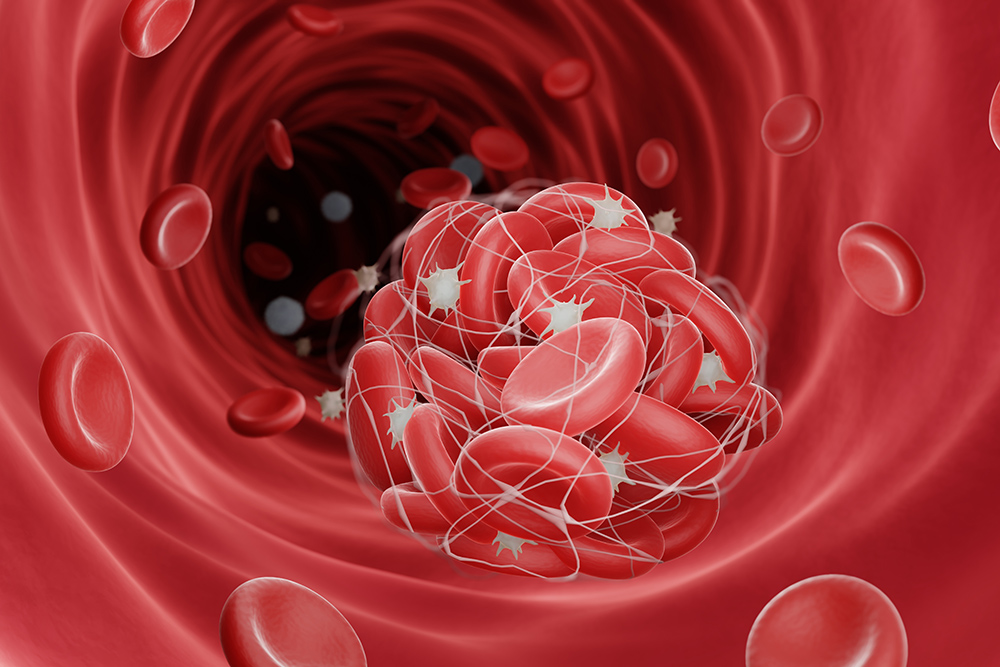
What is the condition of sluggish blood? In terms of the risk of thrombosis, it is likely that platelets and the coagulation system are easily activated and that the fibrinolytic systems are not in normal process. Platelets are the components that work to stop bleeding.
In other words, blood tends to coagulate when platelets are activated, for example, this tendency gets stronger when there is a lot of mental stress.
A blood clot is formed by a web of protein called fibrin, but there are a number of coagulation factors in the blood that are components of the preliminary stage of the final formation of fibrin.
The coagulation system is a population of these coagulation factors, of which an increase in fibrinogen is a major risk factor for thrombosis.
On the contrary, the population of fibrinolytic factors that dissolve thrombi is called a fibrinolytic system. When the inhibitory factor called plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) increases, the fibrinolytic system becomes less active and the clot will be less likely to be dissolved in the blood.
Changes in Blood Vessels
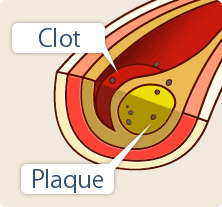
Vascular endothelial (most inner layer of blood vessels) cells work to keep blood from clotting in blood vessels. Therefore, when these cells become inflamed or impaired by atherosclerosis, the blood tends to clot.
In the type of arteriosclerosis in which fatty substances such as cholesterol accumulate in the arterial lining to form plaque and gradually thickens and narrows the arterial lumen, the coagulation system becomes activated all at once when the plaque ruptures. This leads to sudden myocardial infarction or cerebral infarction with a large infarct area.
Changes in Blood Flow
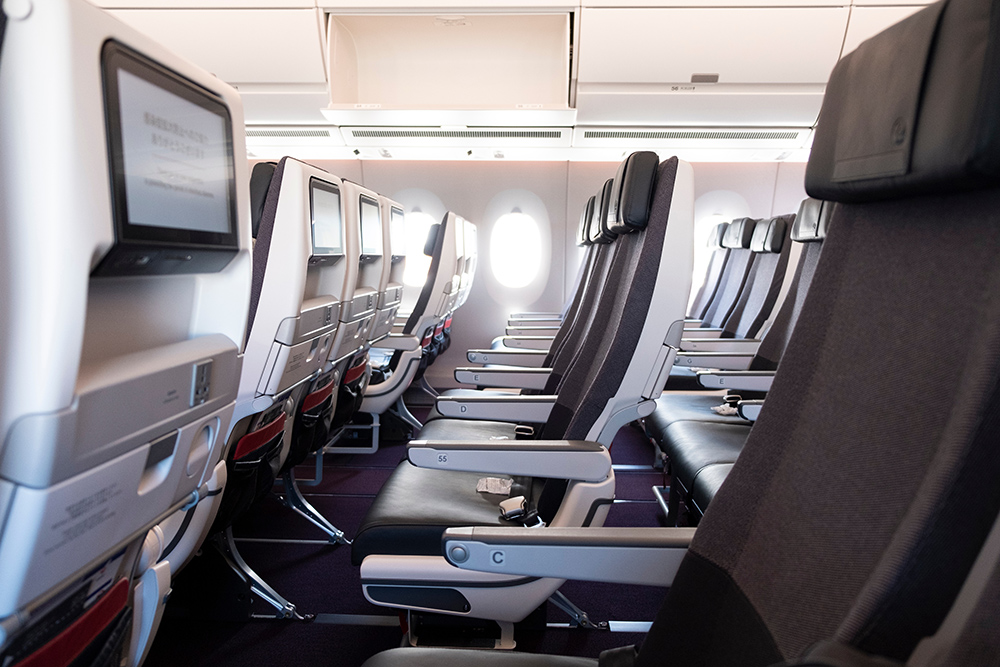

When the blood flows quickly, red blood cells break apart and blood viscosity decreases; when blood flows slowly, red blood cells aggregate with each other and viscosity increases. In other words, slow blood flow makes thrombosis more likely, but how does this velocity in flowing fluid changes?
The velocity of blood flow changes depends on the power of the heart pump and the resistance created by thin arteries as well, however in the veins, the contraction of the calf muscles and the strength caused by breathing exercises also play a major role. Therefore, for example, blood clots can form in the veins due to prolonged immobility in a narrow airplane seat or sleeping in a narrowed car during a disaster.



