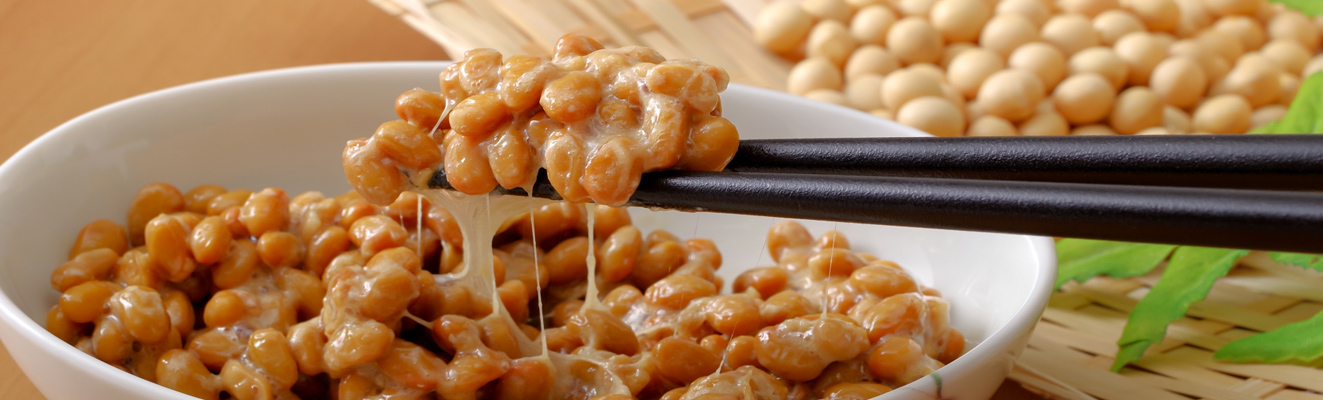
Nattokinase
Vitamin K2

Vitamin K is essential for proper blood coagulation, activating both factors that promote and inhibit blood coagulation. Furthermore, recent studies have revealed that it has very important functions such as activating ''osteocalcin'', a protein that forms bones, and activating ''matrix Gla protein'', a protein that prevents atherosclerosis and heart disease by inhibiting calcium deposition in arteries. It is an essential nutrient for a healthy life. There are two main types of vitamin K: vitamin K1, which is found in vegetables and seaweeds, and vitamin K2, which is produced by microorganisms. While there is only one type of vitamin K1, Vitamin K2 has different lengths of side chains and is called menaquinone. The vitamin K2 found in natto is menaquinone-7 (MK-7), and natto is the highest vitamin K2-containing food in the world. Recent studies have revealed that vitamin K2 = MK-7 in natto is the most nutritious of all vitamin Ks.
Main Functions of Vitamin K2
Factors activated by vitamin K2
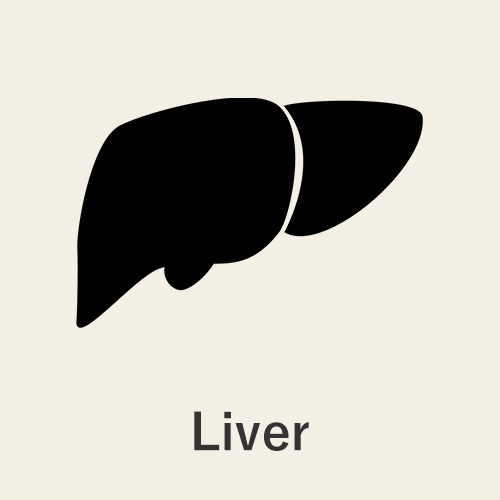
When vitamin K is consumed, it begins with taken up by the liver to promote normal blood coagulation.
・Blood coagulation stimulating factors II, VII, IX, X
・Coagulation inhibitory factors C, S, Z

It activates matrix Gla protein while moving through the blood and prevents deposition of calcium in blood vessels, which can cause atherosclerosis.
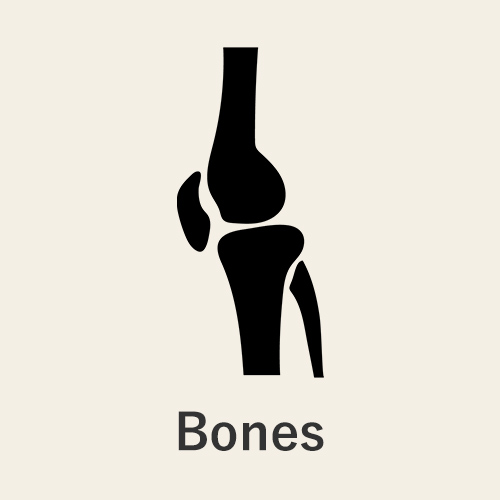
Finally, it activates osteocalcin in the bone marrow and promotes bone formation.
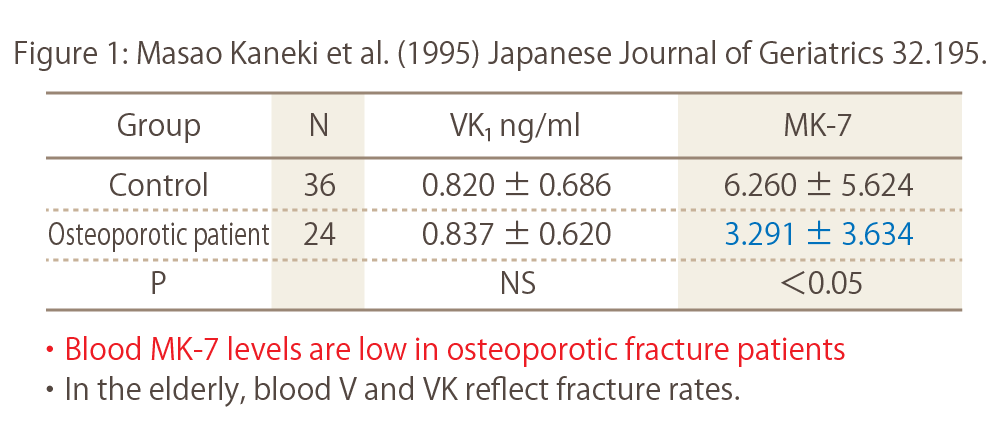
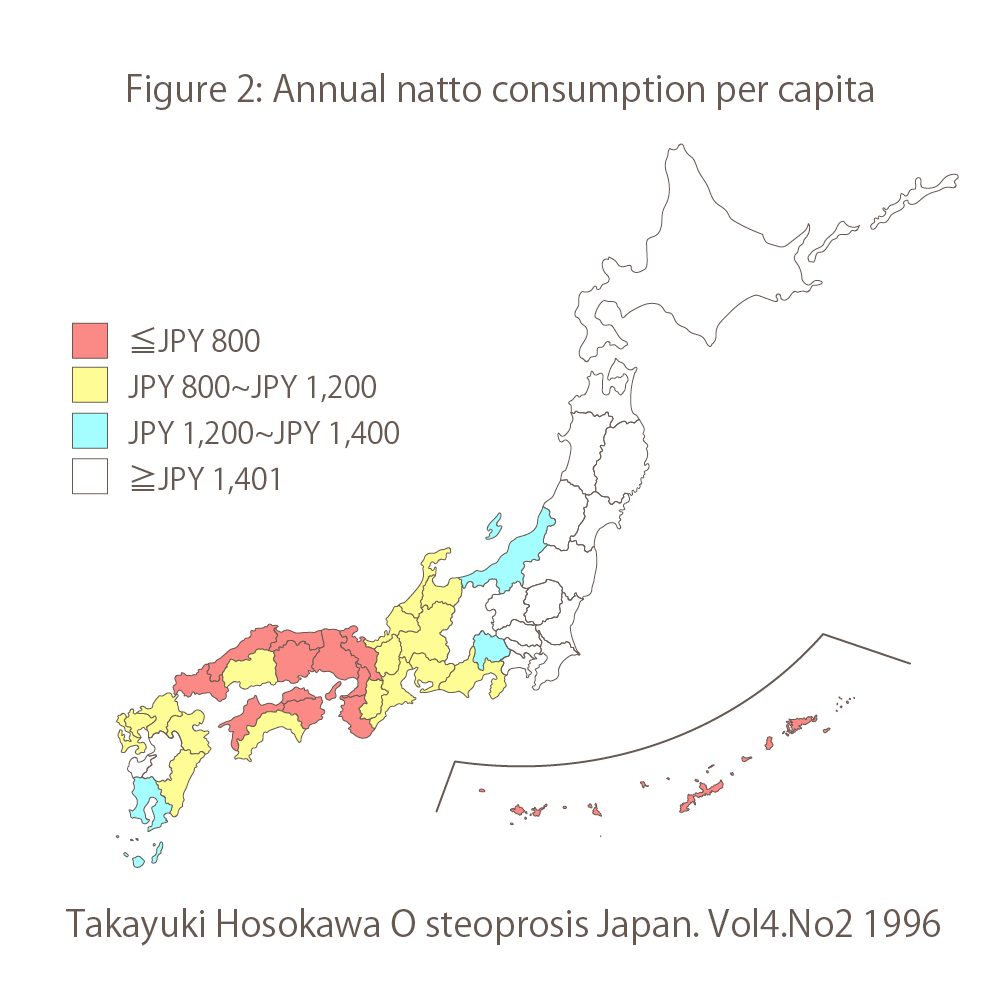
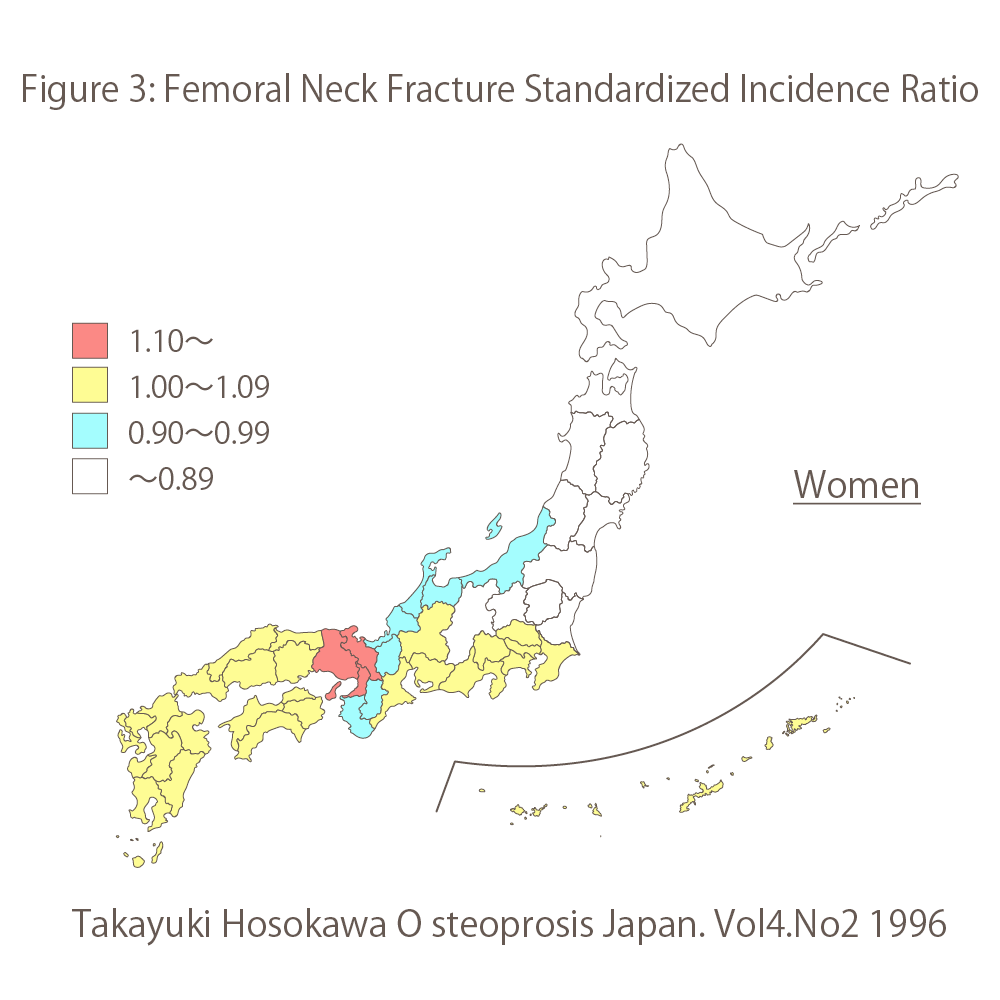
Do you know the amount of calcium in your arteries?

TIME, September 2005
Disease progression of severe asymptomatic aortic aneurysms has been found to be indexed only by calcification of the aortic valve, and age, gender, presence of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia are not indicators of disease onset.
From the Magazine | Health
The Newest Risk Factor
By ALICE PARK
Posted Sunday, Aug. 28, 2005
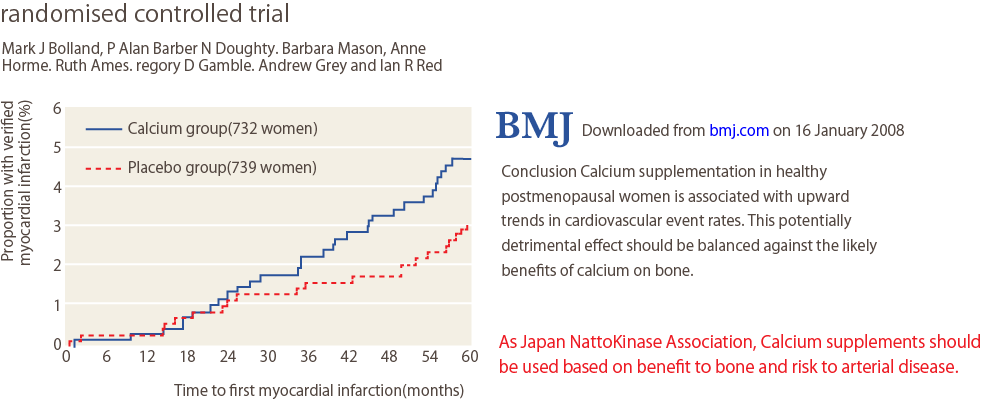
Calcium supplements (1 g) intake is associated with increase of arterial disease.
Vitamin K2 (MK-7) lowers the risk of heart disease
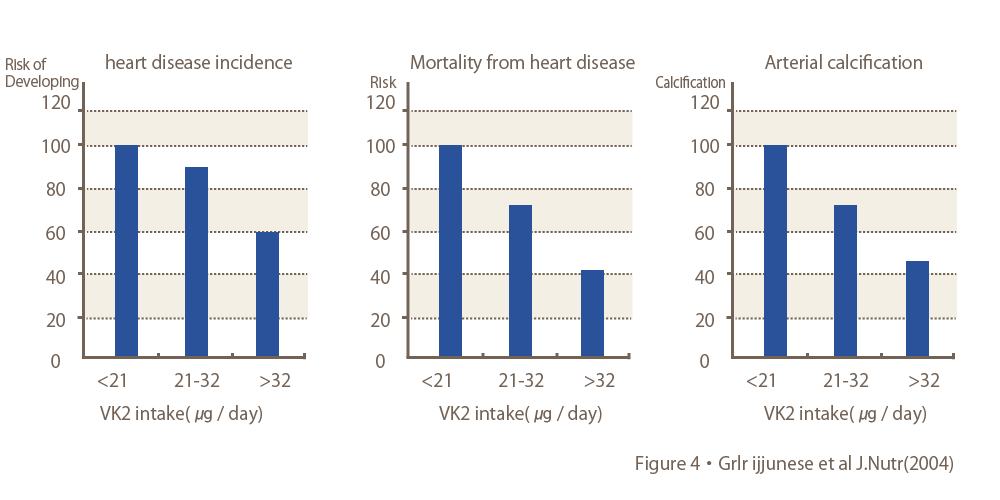
A 10-year study of about 5,000 people in the Netherlands found that the group consuming more vitamin K2 (MK-7) (45 µg per day on average) halved the incidence of heart disease and cardiac mortality compared to the group consuming less (18 µg per day on average). On the other hand, no correlation was found for vitamin K1 in vegetables and seaweeds.
Difference in absorption rate between MK-4 and MK-7
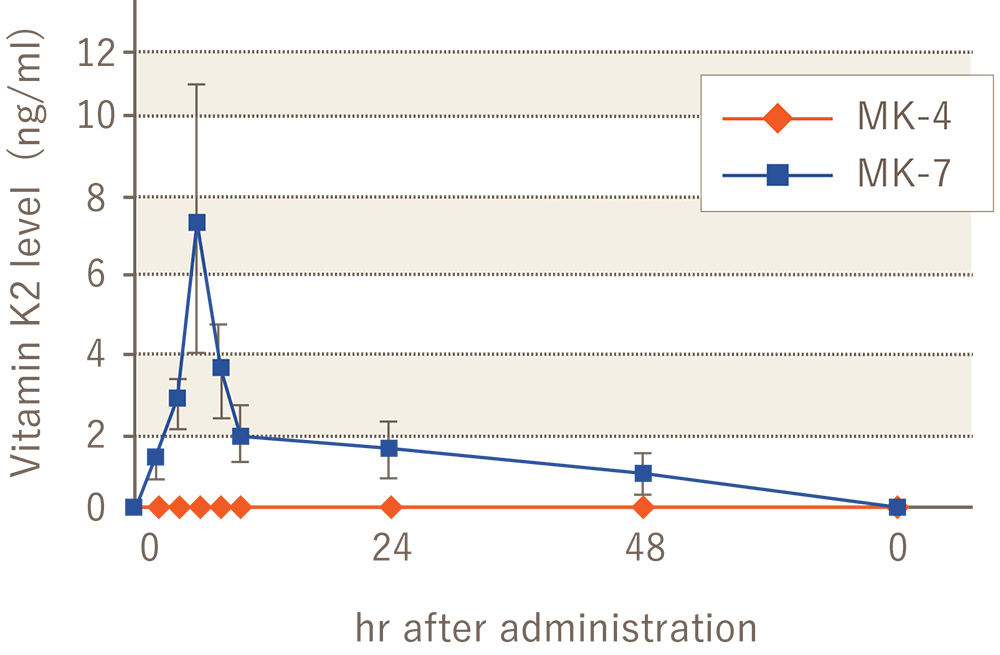
When 420 µg of vitamin K2 was ingested at a time, MK-7 was found to increase the amount in the blood, but MK-4 was not detected in the blood of the group that ingested MK-4. MK-4 has either a low absorption rate or is very fragile and may be broken down by the time it is absorbed from the intestinal tract and reaches the liver.



