Nattokinase
Nattokinase found in the sticky part of Natto
“Natto” is a Japanese traditional food eaten from an ancient time as health food. Nattokinase is a serine protease existed in the sticky part of Natto. Natto is made from steamed soybeans fermented by Bacillus subtilis natto. Nattokinase and other diverse nutrients are produced in this process. In 1925, Dr. Oshima at Hokkaido University (formerly Hokkaido Imperial University) reported its purification and characteristics. Since then, various research report about Nattokinase were made. In the 1980s, the enzyme that degrades (dissolves) fibrin proteins (a cause of thrombi) was named as “Nattokinase”.
Thrombolytic activity of Nattokinase

Functions of Nattokinase include directly degrading (dissolving) a fibrin which is the main component of thrombi, activating pro-urokinase which is a precursor for a thrombolytic enzyme in the body, urokinase, and increasing the amount of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) that produces a thrombolytic enzyme, plasmin. In addition, recent research has revealed that Nattokinase has a function of degrading plasminogen activator inhibitor, PAI-1, and reducing the euglobulin lysis time. Therefore, it has a function of improving the thrombolytic activity.
Nattokinase and Blood Flow Improvement

As stated above, Nattokinase has been confirmed to have the function that directly or indirectly dissolves thrombus, which leads to improve the blood flow in the blood vessels that had been blocked by blood clots. Especially among the elderly, their blood vessels are significantly different from those of younger people both morphologically and functionally. Because of this, it has been reported that the blood flow in these people decreases with age. Nattokinase has been shown in human studies to have a function of improving the blood flow and may reduce these effects of aging. In addition, human studies have also confirmed that by improving blood flow, Nattokinase has the ability to lower blood pressure and maintain peripheral body temperature, which are the significantly important function which Nattokinase has.
*Our recommended raw materials are compatible with Japanese Foods with Functional Claims.
Removal of Vitamin K2 which Promotes Blood Clotting
Natto as food contains “Nattokinase” which helps the thrombus to dissolve, but also contains “Vitamin K2” which promotes blood clotting. Therefore, Nattokinase whose Vitamin K2 is removed has a better thrombolytic activity than Natto does. In addition, those who take “Warfarin”, which is an anticoagulant drug prescribed for thrombosis patients to inhibit blood coagulation, are restrained from eating food by a doctor, that contains a large amount of vitamin K2 such as natto because “the antagonistic activity by Vitamin K2” weakens the effect of warfarin. Therefore, the thrombolytic activity by natto cannot make the best use of it. However, Nattokinase can be safely taken by such people.
Safety of Nattokinase
Because of the unique functions of Nattokinase in dissolving blood clots, its safety must also be strictly investigated. Japanese people traditionally eat natto as a food, and as mentioned above, natto also contains a large amount of vitamin K2, which is related to blood clotting. The Nattokinase recommended by the Japan NattoKinase Association does not contain this vitamin K2, and has passed various safety tests and obtained multiple certifications from overseas. In addition, Nattokinase is characterized by its ability to dissolve blood clots from various angles. For this reason, consumers often ask, “if I take too much Nattokinase, won't it stop bleeding?” however, Nattokinase has passed various safety tests and can be consumed without concerns.
Nattokinase is the most effective when taken after dinner and before bedtime
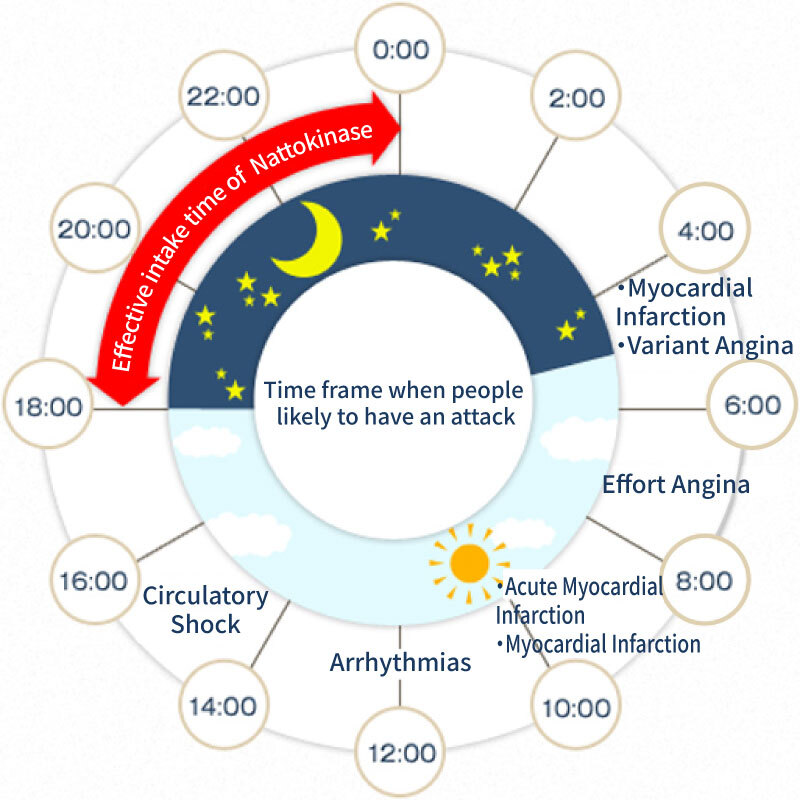
Since blood clots tend to form late at night or early in the morning, the best time to take Nattokinase is after dinner or before bedtime. Regular intake is especially recommended for people in their 40s or older, people under high stress, people with high blood pressure, and people with high blood viscosity due to hyperlipidemia, diabetes, etc.



