Counterfeit Warning
Increase of counterfeit Nattokinase products at overseas
JNKA has approximately 64 member companies from Japan (as of 2024), and approximately 38 member companies from overseas (as of 2024), and these numbers are increasing every year. However, as Nattokinase attracts attention at overseas, many low-priced counterfeit products that safety has not been confirmed or that Nattokinase activity does not meet the standard have appeared, and confusing the market.
Some of these counterfeit products have FU labels that indicate Nattokinase activity that are larger than its actual FU value. There are also malicious products that claim to contain “Nattokinase” although do not contain Nattokinase at all, and instead, contain other enzymes that the safety has not been confirmed (please see below).
Nattokinase is a proteolytic enzyme that specifically degrades only blood clots and confirmed its safety. Others may break down proteins that are necessary for the human body. We recommend that you consume products that have acquired the JNKA mark or products from our member companies.

How to identify Nattokinase - Fibrinolysis Method -

How do we determine if it is Nattokinase or not?
The first step is to identify Nattokinase based on the FU value, which stands for Fibrinolytic Unit. JNKA sets the standard daily dosage requirement as 2000 FU.
There are various methods to measure Nattokinase activity, but we recommend the fibrinolysis method, which can measure FU values. This method is excellent in its reproducible and quantifiable. On the other hand, there is a disadvantage that it cannot accurately measure the activity of Nattokinase alone, since the activity of other enzymes can also be measured.
How to identify Nattokinase - IBox Test ―
Enzymes that cannot be discriminated by the fibrinolysis method are further analyzed by the Nattokinase Simple Discrimination Method (IBox Test).
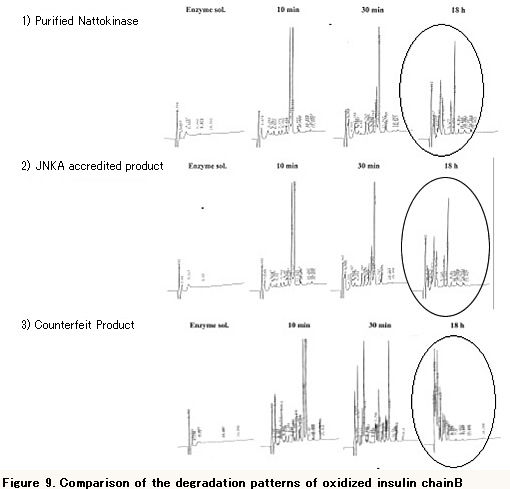
The IBox test is a method of degrading an oxidized insulin chain-B consisting of 30 amino acids with a sample enzyme, and confirm the degradation pattern by HPLC. Since the degradation pattern differs depending on the sample enzyme, it is possible to determine at a glance whether Nattokinase or other enzymes are contained in the sample.
Figure 9 shows the degradation patterns of oxidized insulin chain-B with a purified Nattokinase, a JNKA examined and certified Nattokinase, and a fake Nattokinase product claiming to be Nattokinase. In comparison, the degradation pattern of the fake Nattokinase product is different from that of Nattokinase. Therefore, it is clear that it is not Nattokinase.
How to identify Nattokinase - ELISA method -
Recently, in addition to the above two methods, we have been recommending the ELISA method utilizing antigen-antibody reaction with the cooperation of Dr. Ota, who was a professor at the Department of Pathological Biochemistry from Kobe Pharmaceutical University.
The most important feature of ELISA method is its ability to quantify Nattokinase. As the “Lock-and-key model”, only one antibody reacts with one antigen. Taking advantage of this characteristic of antigen-antibody reaction, Nattokinase can be quantitatively analyzed by measuring the amount of the complex that caused the antigen-antibody reaction using a Nattokinase antibody extracted from a rabbit.
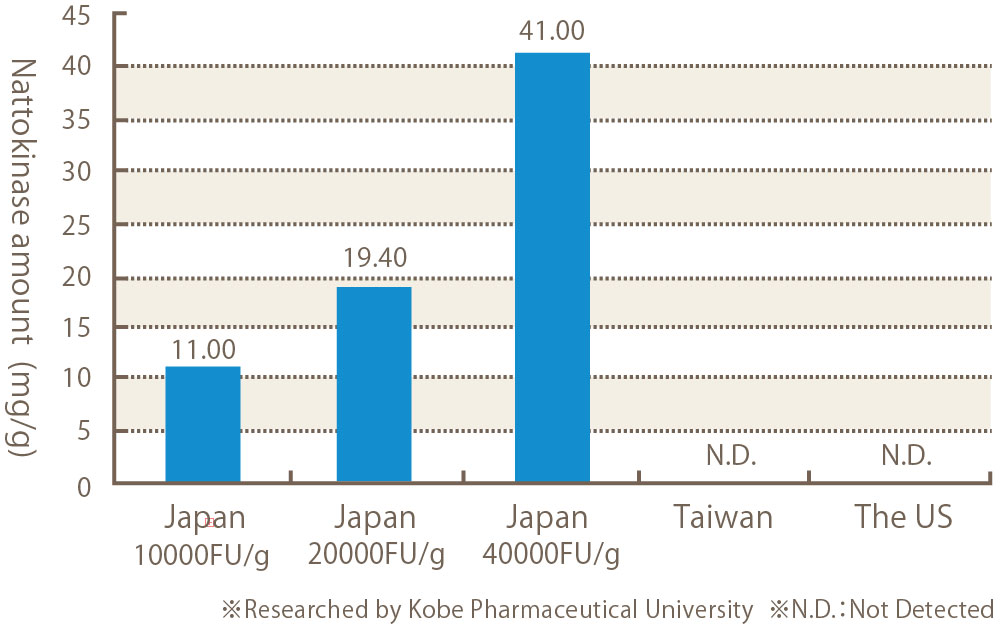
We compared raw materials of Nattokinase made in Japan, Taiwan and the US by using ELISA method. Their results clearly show that raw materials from Japan contain Nattokinase in line with FU activity, while raw materials from the US and Taiwan do not contain any Nattokinase at all.
Counterfeit Products Information
- 2011.10.12 Counterfeit Held a press conference in Taiwan to promote the eradication of counterfeit products!
- 2011.08.23 Counterfeit Beware of counterfeit raw materials made in overseas
- 2010.12.10 Counterfeit An article was published in the December 2010 issue of “常春 Evergreen”, a Taiwanese health magazine
- 2010.12.01 Counterfeit Beware of similar products
- 2010.11.05 Counterfeit TV Broadcast of Nattokinase on China Central Television



